Genetically Modified Crop Breeding and Safe Application Solutions
Transgenic Crop Breeding and Safe Application Technology Solution
Breaking Traditional Breeding Limits · Ensuring Food Security · Promoting Agricultural Sustainability
Program Introduction
This solution employs modern molecular biology techniques to introduce specific exogenous genes into target crops through genetic engineering, cultivating new transgenic crop varieties with superior traits such as pest resistance, stress tolerance, high yield, and quality. The program strictly complies with national biosafety regulations, establishing a comprehensive safety management system covering the entire process from laboratory research to commercial application.
Applicable Regions
- ✓ Major grain production areas (Northeast Plain, North China Plain, Middle-Lower Yangtze Plain, etc.)
- ✓ Arid and semi-arid regions (Northwest China, Inner Mongolia, etc.)
- ✓ Areas with high incidence of pests and diseases (Southern humid regions, etc.)
- ✓ Areas with poor or saline-alkali soils
Applicable Crops
Staple Crops
Rice, Corn, Wheat, Potato
Cash Crops
Cotton, Soybean, Rapeseed
Specialty Crops
Insect-resistant Peppers, Storage-tolerant Tomatoes
Solution Details
1. Gene Mining and Functional Verification
Through genomics, transcriptomics and other methods to mine genes related to pest resistance, stress tolerance, and high yield, using CRISPR/Cas9 and other gene editing technologies for functional verification.
2. Genetic Transformation System Construction
Establish efficient genetic transformation systems for different crops, including Agrobacterium-mediated method and gene gun method, to improve transformation efficiency.
3. Transgenic Plant Cultivation
Screen positive transformants through molecular detection, conduct multiple generations of selfing purification to obtain transgenic lines with stable traits.
4. Safety Evaluation and Regulation
Conduct environmental safety and food safety evaluations according to national "Regulations on Safety Management of Agricultural Genetically Modified Organisms", establishing a whole-process traceability management system.
Technical Highlights
Precision Breeding
Using gene editing technology to achieve precision breeding, significantly shortening the breeding cycle (traditional breeding 8-10 years → transgenic breeding 3-5 years)
Multi-trait Stacking
Can achieve stacking of multiple traits such as insect resistance, disease resistance, and drought tolerance, solving complex stress problems
Safety Control
Establish molecular characteristic detection technology system to achieve accurate detection and traceability of transgenic components
Technology Maturity
Laboratory R&D Stage: 85% Mature
Field Trial Stage: 65% Mature
Commercial Application Stage: 45% Mature
Note: China has approved commercial planting of transgenic insect-resistant cotton and virus-resistant papaya, while staple crops like corn and soybean are undergoing safety evaluation processes.
Case Studies
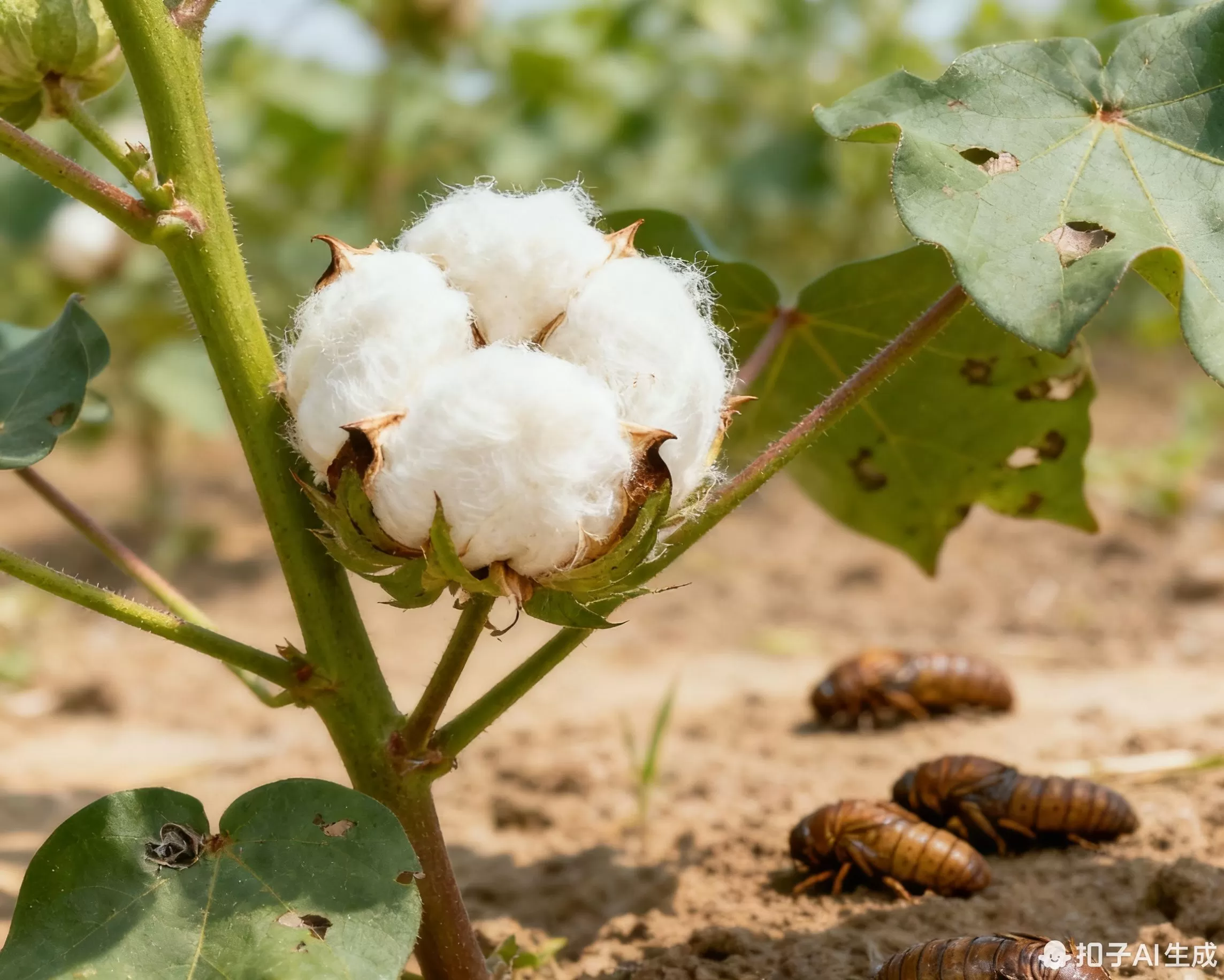

Insect-Resistant Transgenic Cotton
• Planting Area: Accumulated over 4 million hectares
• Technical Effect: Reduced pesticide use by more than 70%
• Economic Benefit: Increased income by 200-300 yuan per mu
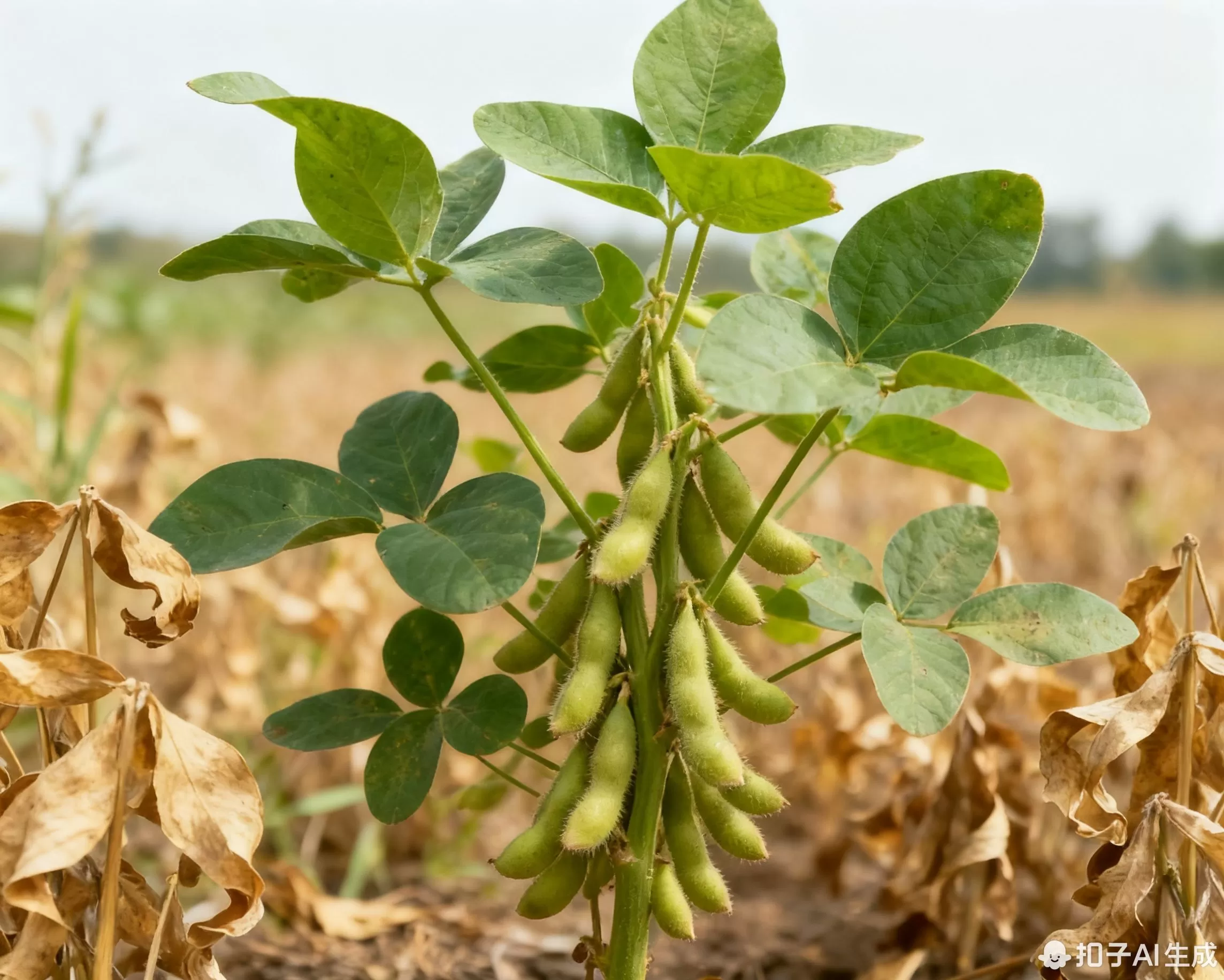

Herbicide-Tolerant Transgenic Soybean
• Trial Yield: 15-20% higher than conventional varieties
• Technical Feature: Glyphosate tolerance, simplified field management
• Application Prospect: Expected to complete safety evaluation by 2026
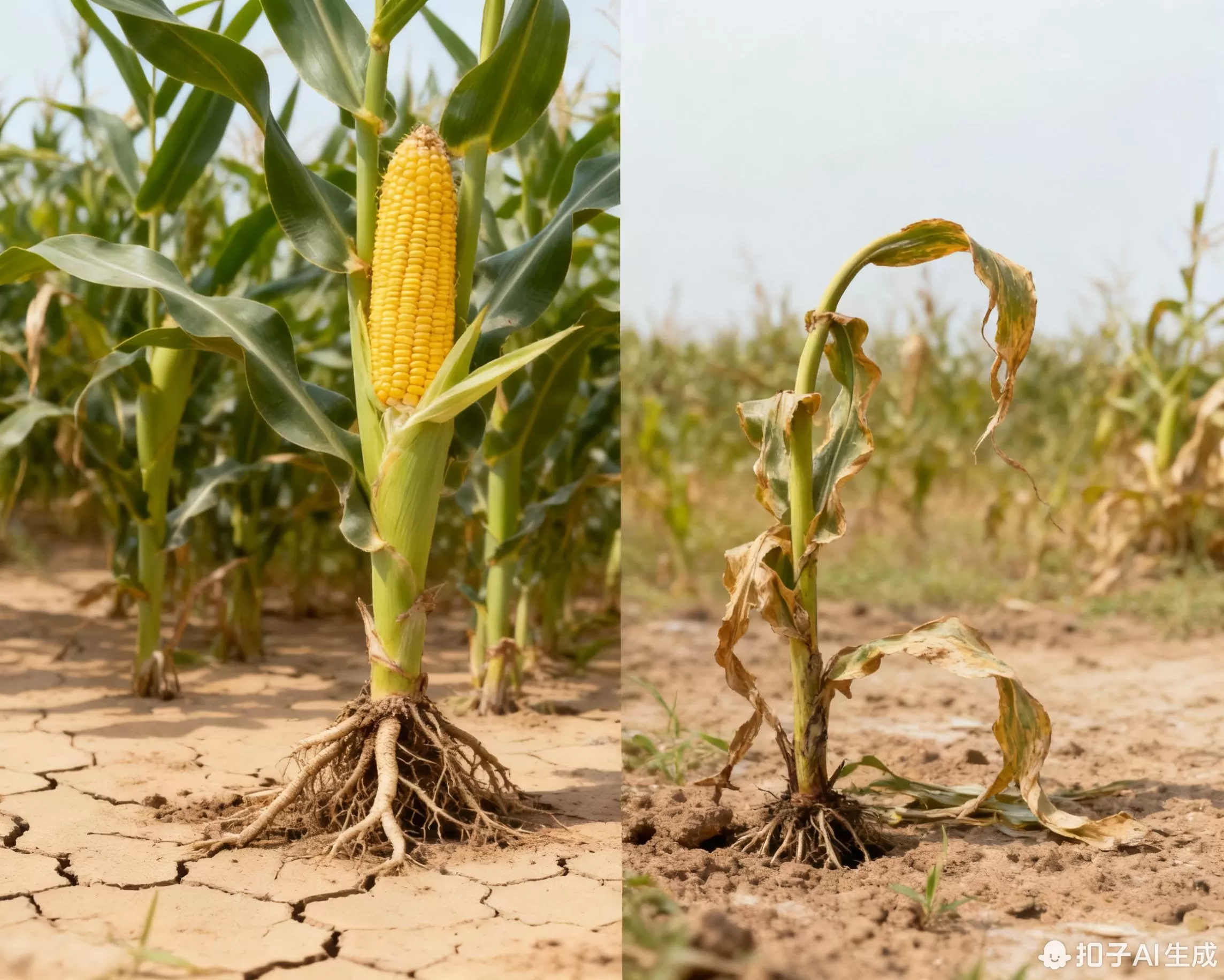

Drought-Tolerant Transgenic Corn
• Trial Performance: 30% yield increase under drought conditions
• Technical Core: Introduction of drought-resistant related genes
• Promotion Area: Demonstration planting in Northwest arid regions